Best FTP client for Mac
- External Hard Drive For Mac Os X 10.7.5
- Onedrive Mac Os
- External Hard Drive For Mac Os 10.6
- How To Format A Hard Drive For Mac Os X
Simple and easy to use, MacDrive is recognized as the leader for accessing Mac disks from Windows for almost 20 years. Once you plug in your Mac disk, behind the scenes MacDrive works to seamlessly enable Windows understand HFS+ disks and allow you to read and write to the disk. This driver provides write access for Seagate external drives in Mac OS without having to reformat. Paragon Driver for Windows The driver provides read and write access for Seagate external drives in Windows without having to reformat. Note: Not compatible with.
A network drive, also known as a NAS (network attached storage) drive, is a storage device that connects to a home or office network instead of your computer. Some of the advantages of this are obvious: for example, you can get access files from a smartphone, tablet, or computer without having to plug the drive in.
Other, perhaps less obvious, positives of NAS include things like automated backups and the ability to mirror data on two drives. In other words, NAS offers a flexible and protected way to manage Mac storage that’s far beyond that of standard external hard drives. Read along to learn how to map a network drive and avoid some common NAS mistakes.
Get the best drive mapping tool
Get Setapp — your easy access to top-notch drive mapping solutions. Map a network drive and connect to another computer instantly.
What is a network drive used for?
Whether it’s populated or diskless, has one bay or more than five, a network drive is typically used as an alternative to cloud storage. It may be easy to drag and drop files to something like Google Drive or Dropbox, but just a bit of drive mapping can make using a network drive a fantastic cloud alternative.
Some of network drive’s key advantages include:
- Better control over your files
- More security features than cloud services
- Flexibility without compromising on privacy
- Being used by multiple users across multiple devices
Map network drive on macOS (one-time)
Nowadays, most NAS devices are seriously easy to map. Let’s say that you’ve been working on a document in your home office but have just remembered a key fact that you want to include. Time to make a quick edit from your wife’s laptop before you forget about it!
Network drive access can be obtained in three simple steps, provided you don’t mind having to repeat those steps if the connection drops, you restart your Mac, or the device is disconnected:
- In Finder, either hit Command+K to bring up “Connect to Server” or click Go > Connect to Server
- Enter the path of the network drive you’re trying to map (e.g. smb://192.168.1.300/shared/Files) and click Connect
- Enter your login details and password then click OK to mount the network drive
You can now access the relevant drive either via your desktop or the sidebar in Finder windows.
Map network drive on macOS (remount after reboot)
Maybe you have a server in your office with a connected network drive and want all your employees to be able to connect to it so they can collaborate on shared documents. If you want to keep a Mac connected to a network drive, even after restarting, the easiest way to do this is to follow the three steps above then add these:
- Hit the Apple menu, then System Preferences > Users & Groups
- From here, select Login Items and click + to add a new item
- Find your network drive and click Add, then close the window
Now, your network drive will be mapped and automatically remounted when you reboot your Mac. Network drives won’t, however, connect automatically if you’re using a different WiFi network.
Make a network drive accessible from Mac desktop
Depending on your settings, mounted drives may not always appear on your desktop. That’s not necessarily a problem if you don’t mind only being able to see connected servers in Finder window sidebars and open/save dialogues.
If, however, you want your NAS device to always be just one double-click away (in the same way that most people have Macintosh HD as a visible item on their desktop) just follow these steps:
- Open Finder > Preferences or click Command + to open Finder Preferences
- Click the General tab, then tick the box next to Connected servers
- Close Finder Preferences
Remount a mapped network drive with one click
Managing, or working across, multiple departments that each have their own network drive? In that case, it can be handy to create aliases of mapped network drive(s):
- Right click on any mapped NAS device on your desktop.
- Select Make Alias
This might not sound like anything all that significant but, as the subheading suggests, you can use this alias to reconnect to a network drive with one click. That can be very helpful if you need to keep jumping between different shared drives.
How to manage files with network-attached storage
In most cases, macOS’s default tools are sufficient for viewing, editing, and deleting files. That might change, however, if you’re using a NAS device. For example, it’s very easy to end up with a ton of duplicate files on your network drive where it’s likely you’ll be less concerned about making the most of your storage as you might be with a built in hard drive.
Gemini is a great tool for digging out any duplicate content on your drives, so you can ditch everything you no longer need while hanging onto backup documents, photos, etc.
- Open up the app and hit the giant + or drag your folder of choice into the window
- Choose from recommended locations or select a custom folder
- Push the green Scan for Duplicates button to get started
- Delete duplicate files manually or use Smart Cleanup to automate the process
For a more granular approach to file management, you might want to consider something like DCommander or Forklift. These apps both offer dual-pane file management, as well as features like batch renaming, copying, and deletion, in a more seamless way than your default Finder.
Although Forklift was designed with FTP management in mind, it’s become a favorite of network drive users because of how closely it resembles macOS. Billed as a Finder replacement app in parts of its marketing material, you won’t find an app much more native unless it comes out of Cupertino.
Plus, actually getting started with the app is incredibly simple:
- Open up the Forklift app
- Use the left-hand panel to find the file(s) you want to move across
- Select the right-hand panel then, using the sidebar, click on your network drive
- Start moving, renaming and archiving files
If Forklift isn’t for you then you might prefer to take a look at DCommander, an approved Mac alternative of Total Commander for Windows. In addition to two side-by-side file panels that look very similar to those of Forklift, DCommander puts a wider range of commands and features (including quick file viewing, selective file unpacking, navigation history, and a great looking Dark Mode) at your fingertips without the need to leave the dual-panel display.
Both apps let you do things like mark certain drives as favorites, create and browse archives, and get previews of items. In short, they’re much like macOS’s Finder … only better. It’s difficult to overstate how much easier it becomes to manage Mac storage with dual-pane browsing until you try to organize your network drive without it!
Unlock the full pack of Mac problem solvers
Get Setapp, a huge set of top apps for keeping your Mac in shape. Best utilities in one pack, give it a go!
Effectively manage Mac storage day-to-day
Thanks to macOS, network drive mapping is a pretty simple process even if you’re not particularly tech-savvy. You might be out of luck if you’re hoping to access a NAS device from another network using standard macOS tools but, at present, that’s pretty much the only thing keeping network drives from competing with the cloud at the mainstream level.
If remote access isn’t such a concern for you and you’re using NAS as an alternative to cloud, then it’s definitely worth taking a look at programs like Forklift or DCommander to make file management easier once you’re done drive mapping, as well as Gemini to ensure that your NAS device isn’t filling up with duplicate files you don’t need.
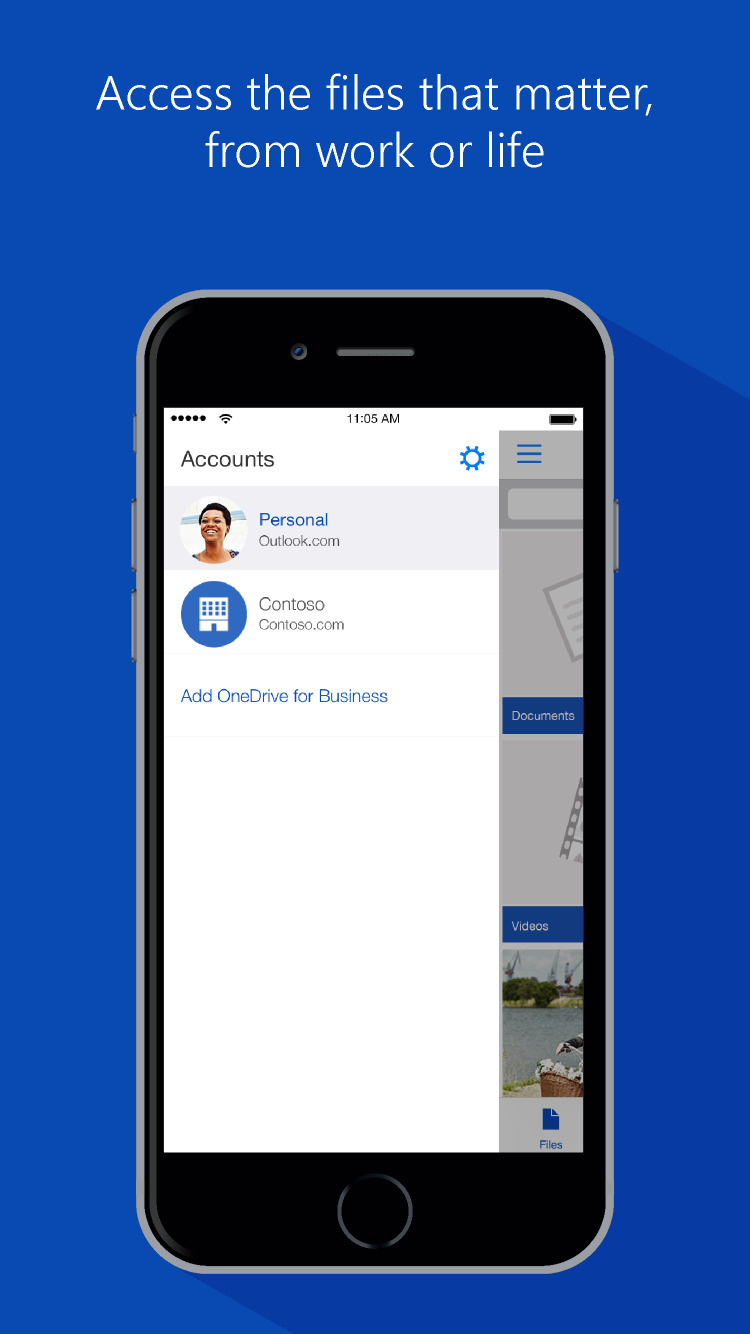
Best of all, the software mentioned above is available for a free trial through Setapp, a collection of over 150 high-quality macOS applications from the best developers around. Manage your Mac effectively today!
External Hard Drive For Mac Os X 10.7.5
Meantime, prepare for all the awesome things you can do with Setapp.
Read onSign Up
Erasing your disk: For most reasons to erase, including when reformatting a disk or selling, giving away, or trading in your Mac, you should erase your entire disk.
Erasing a volume on your disk: In other cases, such as when your disk contains multiple volumes (or partitions) and you don't want to erase them all, you can erase specific volumes on the disk.
Erasing a disk or volume permanently deletes all of its files. Before continuing, make sure that you have a backup of any files that you want to keep.
How to erase your disk
- Start up from macOS Recovery. Then select Disk Utility from the Utilities window and click Continue.
If you're not erasing the disk your Mac started up from, you don't need to start up from macOS Recovery: just open Disk Utility from the Utilities folder of your Applications folder. - Choose View > Show All Devices from the menu bar in Disk Utility. The sidebar now shows your disks (devices) and any containers and volumes within them. The disk your Mac started up from is at the top of the list. In this example, Apple SSD is the startup disk:
- Select the disk that you want to erase. Don't see your disk?
- Click Erase, then complete these items:
- Name: Type the name that you want the disk to have after you erase it.
- Format: Choose APFS or Mac OS Extended (Journaled). Disk Utility shows a compatible format by default.
- Scheme: Choose GUID Partition Map.
- Click Erase to begin erasing your disk and every container and volume within it. You might be asked to enter your Apple ID. Forgot your Apple ID?
- When done, quit Disk Utility.
- If you want your Mac to be able to start up from the disk you erased, reinstall macOS on the disk.
How to erase a volume on your disk
- Start up from macOS Recovery. Then select Disk Utility from the Utilities window and click Continue.
If you're not erasing the volume your Mac started up from, you don't need to start up from macOS Recovery: just open Disk Utility from the Utilities folder of your Applications folder. - In the sidebar of Disk Utility, select the volume that you want to erase. The volume your Mac started up from is named Macintosh HD, unless you changed its name. Don't see your volume?
- Click Erase, then complete these items:
- Name: Type the name that you want the volume to have after you erase it.
- Format: Choose APFS or Mac OS Extended (Journaled). Disk Utility shows a compatible format by default.
- If you see an Erase Volume Group button, the volume you selected is part of a volume group. In that case, you should erase the volume group. Otherwise, click Erase to erase just the selected volume. You might be asked to enter your Apple ID. Forgot your Apple ID?
- When done, quit Disk Utility.
- If you want your Mac to be able to start up from the volume you erased, reinstall macOS on that volume.
Reasons to erase
You can erase at any time, including in circumstances such as these:
- You want to permanently erase all content from your Mac and restore it to factory settings. This is one of the final steps before selling, giving away, or trading in your Mac.
- You're changing the format of a disk, such as from a PC format (FAT, ExFAT, or NTFS) to a Mac format (APFS or Mac OS Extended).
- You received a message that your disk isn't readable by this computer.
- You're trying to resolve a disk issue that Disk Utility can't repair.
- The macOS installer doesn't see your disk or can't install on it. For example, the installer might say that your disk isn't formatted correctly, isn't using a GUID partition scheme, contains a newer version of the operating system, or can't be used to start up your computer.
- The macOS installer says that you may not install to this volume because it is part of an Apple RAID.
About APFS and Mac OS Extended
Disk Utility in macOS High Sierra or later can erase using either the newer APFS (Apple File System) format or the older Mac OS Extended format, and it automatically chooses a compatible format for you.
How to choose between APFS and Mac OS Extended
Onedrive Mac Os
Disk Utility tries to detect the type of storage and show the appropriate format in the Format menu. If it can't, it chooses Mac OS Extended, which works with all versions of macOS. If you want to change the format, answer these questions:
- Are you formatting the disk that came built into your Mac?
If the built-in disk came APFS-formatted, Disk Utility suggests APFS. Don't change it to Mac OS Extended. - Are you about to install macOS High Sierra or later for the first time on the disk?
If you need to erase your disk before installing High Sierra or later for the first time on that disk, choose Mac OS Extended (Journaled). During installation, the macOS installer decides whether to automatically convert to APFS—without erasing your files. - Are you preparing a Time Machine backup disk or bootable installer?
Choose Mac OS Extended (Journaled) for any disk that you plan to use as a Time Machine backup disk or as a bootable installer. - Will you be using the disk with another Mac?
If the other Mac isn't using macOS High Sierra or later, choose Mac OS Extended (Journaled). Earlier versions of macOS don't work with APFS-formatted volumes.
How to identify the format currently in use
If you want to know which format is currently in use, use any of these methods:
- Select the volume in the Disk Utility sidebar, then check the information shown on the right. For more detail, choose File > Get Info from the Disk Utility menu bar.
- Open System Information and select Storage in the sidebar. The File System column on the right shows the format of each volume.
- Select the volume in the Finder, then choose File > Get Info from the menu bar. The Get Info window shows the Format of that volume.
External Hard Drive For Mac Os 10.6
If your disk or volume doesn't appear, or the erase fails
How To Format A Hard Drive For Mac Os X
- Shut down your Mac, then unplug all nonessential devices from your Mac.
- If you're erasing an external drive, make sure that it's connected directly to your Mac using a cable that you know is good. Then turn the drive off and back on.
- If your disk or volume still doesn't appear in Disk Utility, or Disk Utility reports that the erase process failed, your disk or Mac might need service. If you need help, please contact Apple Support.
Learn more
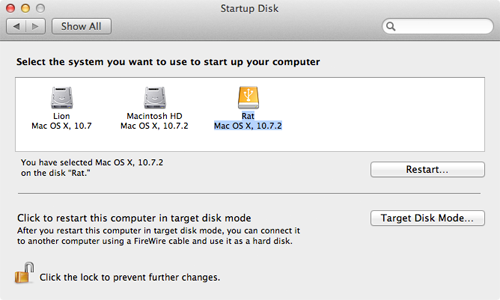
- If you can't start up from macOS Recovery, you can use a different startup disk instead.
- If Disk Utility shows a Security Options button in the Erase window, you can click that button to choose between a faster (but less secure) erase and a slower (but more secure) erase. Some older versions of Disk Utility offer the option to zero all data instead. These secure-erase options aren't offered or needed for solid-state drives (SSDs) and flash storage.
